 The subset relation defines a partial order on sets. In fact, the subsets of a given set form a Boolean algebra under the subset relation, in which the join and meet are given by intersection and union, and the subset relation itself is the Boolean inclusion relation.
The subset relation defines a partial order on sets. In fact, the subsets of a given set form a Boolean algebra under the subset relation, in which the join and meet are given by intersection and union, and the subset relation itself is the Boolean inclusion relation.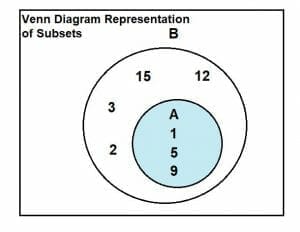 A subset, as the name suggests, is a subcollection of any set. Let us assume we have two sets, X and Y. Mathematically speaking, X will be a subset of Y if and only if all the elements of X are present in Y.
A subset, as the name suggests, is a subcollection of any set. Let us assume we have two sets, X and Y. Mathematically speaking, X will be a subset of Y if and only if all the elements of X are present in Y.